Comprehensive Review of Pest Control Strategies: Ensuring a Pest-Free Environment
Pest control strategies encompass a range of methods and practices aimed at managing and eliminating pests to protect human health, agriculture, and property. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach that combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools to minimize pest damage sustainably. Biological control involves using natural predators or parasites to control pest populations, while cultural strategies focus on altering farming practices to reduce pest attraction. Physical methods include traps and barriers, while chemical control involves the careful application of pesticides when necessary. Effective pest control prioritizes environmental health and safety, aiming to reduce reliance on harmful chemicals and encourage ecological balance by understanding pest life cycles and habitat requirements. This comprehensive approach ensures long-term pest management solutions.
Pest control is an essential aspect of maintaining a clean, safe, and healthy living environment. The presence of pests such as rodents, insects, and other unwanted creatures can lead to various problems, including health risks, structural damage, and psychological discomfort. Over the years, various pest control strategies have been developed and refined to address these issues effectively. This review provides an in-depth analysis of different pest control strategies, evaluating their effectiveness, advantages, and potential drawbacks.
1. Chemical Pest Control
Chemical pest control is one of the most widely used methods due to its effectiveness and rapid action. This strategy involves the use of pesticides and insecticides to eliminate pests. These chemicals can be applied in various forms, including sprays, baits, and powders.
Advantages:
- Immediate Results: Chemical treatments often provide quick and visible results, making them ideal for severe infestations.
- Broad-Spectrum Efficacy: Many chemical pesticides are designed to target a wide range of pests, making them versatile.
- Ease of Use: Commercially available pesticides are generally easy to apply, and many come with clear instructions for homeowners.
Drawbacks:
- Health Risks: Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals can pose health risks to humans and pets. This is particularly concerning in households with children or individuals with respiratory issues.
- Environmental Impact: Chemical run-off can contaminate soil and water sources, leading to broader ecological consequences.
- Resistance Development: Over time, pests can develop resistance to chemical treatments, rendering them less effective.
2. Biological Pest Control
Biological pest control involves the use of natural predators or parasites to manage pest populations. This method is often employed in agricultural settings but can also be applied in residential areas.
Advantages:
- Environmentally Friendly: This strategy minimizes the environmental impact, as it relies on natural processes rather than synthetic chemicals.
- Sustainable: Biological control can provide long-term solutions, as natural predators can establish themselves in the environment and continually manage pest populations.
- Safety: It poses minimal health risks to humans and pets.
Drawbacks:
- Time-Consuming: The results from biological control can take longer to manifest compared to chemical treatments.
- Complexity: Implementing biological control requires a good understanding of the ecosystem and the specific relationships between pests and their natural enemies.
- Limited Scope: This method is often more effective for specific pests and may not be suitable for all types of infestations.
3. Mechanical Pest Control
Mechanical pest control involves the use of physical barriers, traps, and manual removal to manage pest populations. Common methods include the use of mousetraps, insect screens, and fly swatters.
Advantages:
- Immediate and Visible Results: Mechanical methods often provide quick results, especially in the case of traps.
- Non-Toxic: These methods do not involve chemicals, making them safe for humans and pets.
- Targeted Approach: Mechanical control can be highly targeted, reducing the risk of affecting non-target species.
Drawbacks:
- Labor-Intensive: This method can be time-consuming and requires ongoing effort to maintain effectiveness.
- Limited Scope: Mechanical control may not be practical for large infestations or certain types of pests that are difficult to capture or exclude.
4. Cultural Pest Control
Cultural pest control involves modifying the environment or human practices to reduce pest populations. This can include crop rotation, proper waste management, and maintaining cleanliness to deter pests.
Advantages:
- Preventative: Cultural methods focus on preventing infestations rather than reacting to them, which can be more effective in the long term.
- Low Cost: Many cultural practices are inexpensive and can be implemented with minimal investment.
- Environmentally Friendly: These methods typically have a low environmental impact and can enhance the overall health of the ecosystem.
Drawbacks:
- Slow Results: The benefits of cultural control may take time to become apparent.
- Behavioral Changes: Implementing these methods often requires changes in human behavior, which can be challenging to maintain consistently.
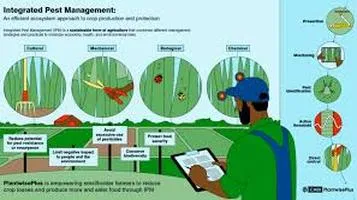
5. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach that combines multiple strategies to manage pest populations effectively. IPM involves monitoring pest populations, setting action thresholds, and employing a combination of biological, chemical, mechanical, and cultural methods.
Advantages:
- Comprehensive: IPM provides a balanced approach, using the strengths of various methods to achieve optimal results.
- Sustainable: By reducing reliance on chemical treatments, IPM promotes long-term sustainability.
- Adaptive: IPM strategies can be adjusted based on ongoing monitoring and feedback, making them flexible and responsive to changing conditions.
Drawbacks:
- Complex Implementation: IPM requires a thorough understanding of pest behavior, monitoring techniques, and the various control methods, which can be challenging for laypersons.
- Initial Investment: The upfront costs of setting up an IPM program can be higher than single-method strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, each pest control strategy has its own set of advantages and drawbacks. The choice of method depends on various factors, including the type of pest, the severity of the infestation, environmental considerations, and the specific needs of the affected area. While chemical methods offer quick results, they come with health and environmental risks. Biological and cultural methods are more sustainable but may take longer to show results. Mechanical control provides immediate action but requires ongoing effort. Integrated Pest Management stands out as a comprehensive and adaptive approach that leverages the strengths of multiple strategies for effective and sustainable pest control. For those seeking a long-term solution with minimal environmental impact, IPM is often the best choice, despite its complexity and initial costs. Ultimately, the most effective pest control strategy is one that is tailored to the specific situation, balancing efficacy, safety, and sustainability.






