Niacinamide: A Comprehensive Review
Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3 or nicotinamide, is a versatile skincare ingredient renowned for its multitude of benefits. It is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin. Niacinamide is celebrated for its ability to improve skin texture, enhance the skin barrier, and reduce the appearance of enlarged pores. It also helps to regulate oil production, making it beneficial for those with oily or acne-prone skin. Additionally, it possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe redness and irritation. Niacinamide is effective in brightening skin tone, diminishing fine lines, and reducing hyperpigmentation. Its gentle nature makes it suitable for all skin types, and it can be easily incorporated into a daily skincare routine for a radiant, balanced complexion.
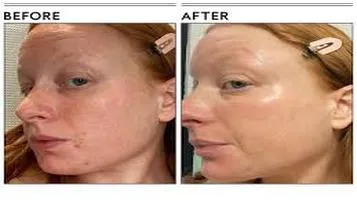
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is a form of vitamin B3 that has garnered significant attention in the skincare and health industries for its versatile benefits. Known for its ability to address a multitude of skin concerns, niacinamide has become a staple ingredient in many cosmetic and therapeutic formulations. This review aims to provide an in-depth analysis of niacinamide, its benefits, mechanisms of action, and potential drawbacks, offering a well-rounded perspective on this multifaceted compound.
What is Niacinamide?
Niacinamide is a water-soluble vitamin that is part of the B-complex group. It is found naturally in foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and green vegetables, and can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Unlike its counterpart, niacin (nicotinic acid), niacinamide does not cause flushing, making it more suitable for cosmetic and dermatological applications.
Mechanism of Action
Niacinamide works through several mechanisms to improve skin health:
1. Barrier Function Improvement: Niacinamide enhances the production of ceramides, which are lipids that maintain the skin's barrier function. A stronger barrier helps to retain moisture and protect against environmental irritants.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Niacinamide has been shown to reduce inflammation, making it beneficial for conditions like acne, rosacea, and eczema.
3. Antioxidant Effects: It helps to fight free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which can lead to premature aging and skin damage.
4. Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide can help to regulate oil production, making it particularly useful for those with oily or acne-prone skin.
5. Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It inhibits the transfer of melanosomes, thereby reducing age spots and hyperpigmentation.
Benefits of Niacinamide
1. Moisturization and Hydration: Niacinamide boosts the skin’s ability to retain moisture, making it an excellent ingredient for hydrating serums and creams. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with dry or sensitive skin.
2. Anti-Aging Properties: By enhancing the skin’s barrier function and reducing oxidative stress, niacinamide helps to smooth fine lines and wrinkles. Its ability to stimulate collagen production further contributes to its anti-aging benefits.
3. Acne Treatment: The anti-inflammatory properties of niacinamide make it effective in reducing the redness and swelling associated with acne. Additionally, its sebum-regulating capabilities help to prevent the formation of new acne lesions.
4. Hyperpigmentation and Uneven Skin Tone: Niacinamide is effective in lightening dark spots and evening out skin tone. It is often included in formulations aimed at reducing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and melasma.
5. Reduction of Pore Size: Regular use of niacinamide can lead to a visible reduction in pore size, giving the skin a smoother, more refined appearance.
Clinical Evidence
Numerous studies have supported the efficacy of niacinamide in skin care. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that a 5% niacinamide formulation significantly improved skin elasticity, fine lines, and wrinkles over a 12-week period. Another study in the British Journal of Dermatology demonstrated that niacinamide was effective in reducing the severity of melasma in patients.
Potential Drawbacks
While niacinamide is generally well-tolerated, it is not entirely free from potential side effects. Some individuals may experience mild irritation, redness, or itching, particularly when using high concentrations. It is advisable to perform a patch test before incorporating niacinamide into your routine. Additionally, niacinamide can sometimes interact with other active ingredients, such as vitamin C, although recent studies suggest that the interaction may not be as significant as previously thought.
Formulations and Usage
Niacinamide is available in a variety of formulations, including serums, moisturizers, toners, and masks. It is often combined with other beneficial ingredients like hyaluronic acid, peptides, and antioxidants to enhance its efficacy. For best results, it is recommended to use niacinamide consistently, typically twice daily, as part of a comprehensive skincare routine.
Conclusion
Niacinamide is a powerhouse ingredient that offers a wide range of benefits for various skin types and concerns. Its ability to improve barrier function, reduce inflammation, and address hyperpigmentation makes it a versatile addition to any skincare regimen. Supported by a robust body of clinical evidence, niacinamide stands out as a reliable and effective option for improving skin health. However, as with any active ingredient, individual responses can vary, so it is essential to monitor your skin’s reaction and adjust usage accordingly.
In summary, niacinamide is a well-researched and highly effective component in the world of skincare, offering multiple benefits with minimal drawbacks. Whether you are dealing with acne, aging, or simply seeking to improve your skin's overall appearance, niacinamide is certainly worth considering.






