The Efficacy and Importance of Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a vital nutrient that plays an essential role in maintaining overall health. It is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, thereby supporting the immune system. Vitamin C is crucial for the synthesis of collagen, a protein necessary for the health and repair of skin, blood vessels, bones, and connective tissues. It also aids in the absorption of iron from plant-based foods, enhancing blood health and preventing anemia. As the human body cannot produce or store vitamin C, it must be obtained through diet, with rich sources including citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli. Adequate intake of vitamin C is important for preventing deficiencies that can lead to scurvy.
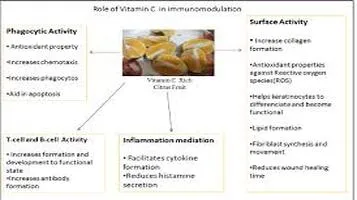
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is an essential nutrient that has garnered significant attention for its myriad health benefits. Its role in the human body is multifaceted, contributing to various physiological processes that range from bolstering the immune system to acting as an antioxidant. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the efficacy and importance of Vitamin C, drawing on scientific research and clinical studies.
Chemical Nature and Sources
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, meaning it dissolves in water and is not stored in the body. It is found in various fruits and vegetables, with citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits being particularly rich sources. Other notable sources include strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, and spinach. Given its water-soluble nature, Vitamin C must be consumed regularly through diet or supplements, as the body does not retain it over time.
Biological Functions
Antioxidant Properties
One of the most well-documented roles of Vitamin C is its function as an antioxidant. It helps neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and diseases such as cancer and heart disease. By mitigating oxidative stress, Vitamin C helps maintain cellular integrity and function.
Immune Support
Vitamin C is perhaps best known for its role in supporting the immune system. It stimulates the production and function of white blood cells, including lymphocytes and phagocytes, which help protect the body against infections. Moreover, Vitamin C enhances the skin's barrier function and promotes the healing of wounds by facilitating collagen formation, a protein essential for skin, cartilage, and bone health.
Collagen Synthesis
Collagen is a structural protein that is crucial for the maintenance and repair of tissues. Vitamin C is a cofactor in the synthesis of collagen, meaning it is necessary for the enzymes that produce collagen to function correctly. This makes Vitamin C vital for skin health, wound healing, and the maintenance of cartilage, bones, and teeth.
Absorption of Iron
Vitamin C enhances the absorption of non-heme iron, the type of iron found in plant-based foods. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, as it helps prevent iron deficiency anemia. By converting iron into a form that is more easily absorbed by the body, Vitamin C ensures that sufficient iron levels are maintained for the production of red blood cells and the transportation of oxygen throughout the body.
Recommended Intake and Supplementation
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for Vitamin C varies by age, gender, and life stage. For adult men, the RDA is 90 mg per day, while for adult women, it is 75 mg per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as smokers, may require higher intakes due to increased physiological demands and oxidative stress.
Vitamin C supplements are widely available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, powders, and chewables. While it is generally best to obtain nutrients from food, supplementation can be beneficial for individuals with increased needs or limited access to fresh fruits and vegetables.
Clinical Evidence and Health Benefits
Cold Prevention and Treatment
One of the most common uses of Vitamin C is in the prevention and treatment of the common cold. While research findings are mixed, some studies suggest that regular Vitamin C supplementation can reduce the duration and severity of colds, particularly in individuals under physical stress or in cold environments. However, for the general population, taking Vitamin C after the onset of symptoms does not appear to have a significant impact on the course of the illness.
Chronic Disease Prevention
Emerging research indicates that Vitamin C may play a role in the prevention of chronic diseases. Its antioxidant properties help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are underlying factors in conditions such as heart disease, hypertension, and certain cancers. Some studies have found that higher plasma levels of Vitamin C are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality.
Skin Health
Topical and oral Vitamin C has gained popularity in dermatology for its anti-aging benefits. It helps reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and hyperpigmentation by promoting collagen synthesis and protecting against UV-induced damage. Clinical trials have shown that Vitamin C can improve skin texture and tone, making it a valuable ingredient in skincare formulations.
Safety and Side Effects
Vitamin C is generally considered safe, with a low risk of toxicity. The tolerable upper intake level (UL) for adults is set at 2,000 mg per day. Excessive intake can lead to gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney stones or hemochromatosis, should exercise caution and consult a healthcare provider before taking high doses of Vitamin C.
Conclusion
Vitamin C is a vital nutrient with a broad spectrum of health benefits. Its antioxidant properties, role in collagen synthesis, immune support, and enhancement of iron absorption underscore its importance in maintaining overall health. While a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables is the best way to ensure adequate Vitamin C intake, supplements can be a useful adjunct for individuals with increased needs or dietary limitations. Given its safety profile and potential benefits, Vitamin C remains a cornerstone of nutritional health and wellness.
In summary, Vitamin C is not just a simple vitamin; it is a cornerstone of health that plays a crucial role in various physiological functions and disease prevention. Its importance cannot be overstated, making it a vital component of a balanced diet and a key player in the realm of nutritional supplements.






